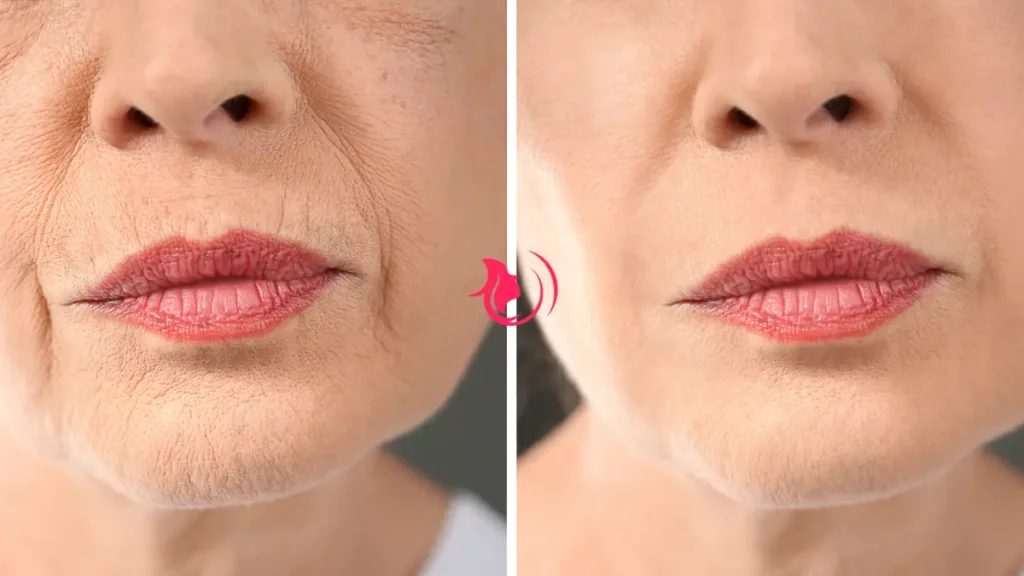
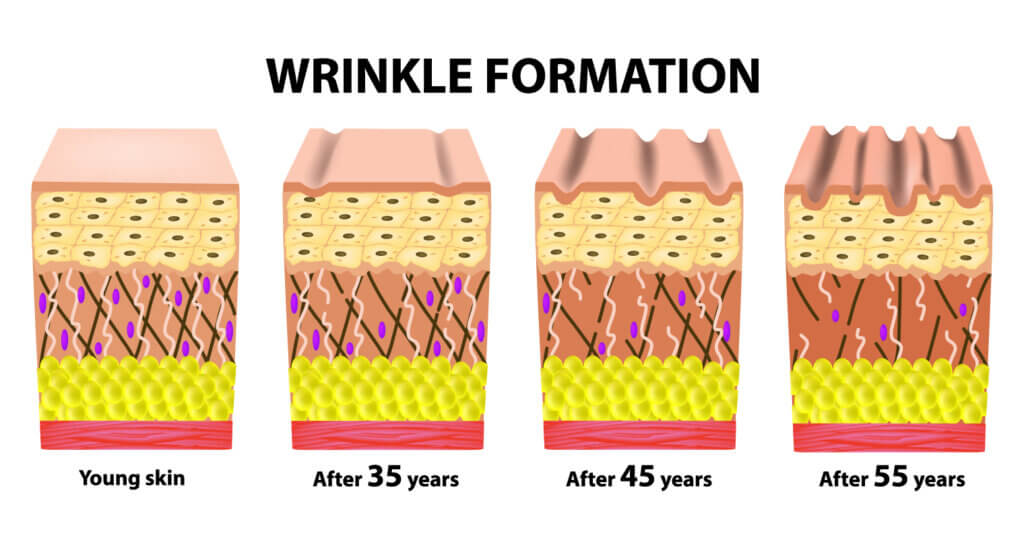
Wrinkles are a natural part of the ageing process and are caused by a combination of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic ageing, also known as chronological ageing, is the natural ageing process that takes place over the years regardless of external influences. This type of ageing is genetically determined and leads to the gradual loss of collagen and elastin, proteins that provide the skin with structure and elasticity. As the production of these proteins decreases, the skin becomes thinner, less resilient, and more prone to sagging and wrinkling.
Extrinsic ageing, on the other hand, is influenced by external factors such as UV radiation, pollution, lifestyle choices, and environmental exposures. UV radiation from the sun, in particular, is a major contributor to premature ageing and wrinkles, a process known as photoageing. UV rays penetrate the skin and damage collagen fibres, leading to the breakdown of collagen and the formation of abnormal elastin. This triggers the production of enzymes called metalloproteinases, which further degrade collagen. Additionally, free radicals generated by UV exposure cause oxidative stress, damaging skin cells and accelerating the ageing process.
Other extrinsic factors include smoking, which reduces blood flow to the skin and accelerates collagen breakdown; poor diet, which lacks the nutrients necessary for skin repair and regeneration; and repetitive facial expressions, which create dynamic wrinkles that become more permanent over time.
The Structure Of The Skin And Collagen Breakdown
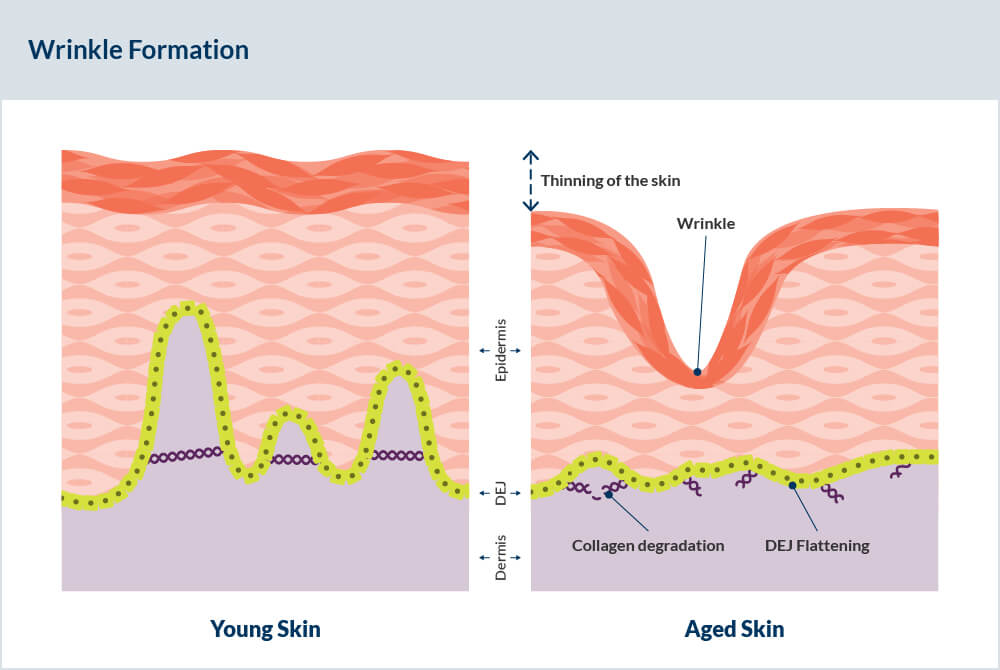
To understand how wrinkles form, it is essential to know a little about the skin’s structure. Our skin is made up of three layers: the epidermis (outer layer), the dermis (middle layer), and the subcutaneous layer (innermost layer). The dermis contains proteins like collagen and elastin, which are responsible for maintaining the skin’s structure, firmness, and elasticity.
Collagen, the most abundant protein in the human body, plays a vital role in keeping the skin looking youthful and smooth. As we age, our body’s production of collagen slows down, and existing collagen begins to break down. This decrease in collagen leads to a weakening of the skin’s support system, resulting in the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Additionally, the skin’s ability to repair itself diminishes, making it less resilient to environmental stressors.
The Latest Advancements In The Treatment Of Wrinkles
The field of dermatology and aesthetic medicine has seen significant advancements in the treatment of wrinkles. Here are some of the latest developments:
- Non-Invasive Skin Tightening: Technologies like radiofrequency (RF), ultrasound, and laser treatments have become popular for non-invasive skin tightening and wrinkle reduction. These treatments stimulate collagen production by delivering heat or energy to the deeper layers of the skin without damaging the surface. Examples include Ultherapy (ultrasound), Thermage (radiofrequency), and fractional laser treatments.
- Injectable Treatments: Botulinum toxin (Botox) and dermal fillers remain popular and highly effective treatments for addressing both dynamic and static wrinkles. Botox works by temporarily paralysing the underlying muscles responsible for causing dynamic wrinkles, such as those that appear with facial expressions. Meanwhile, dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid, not only add volume to the skin but also smooth out deeper lines and folds that develop with age. Additionally, fillers can restore lost volume and fill in hollow areas of the face, giving a more youthful and refreshed appearance.
- Topical Treatments: Advances in skincare have resulted in more effective anti-ageing creams and serums. Key ingredients like retinoids (vitamin A derivatives), peptides, and growth factors help boost collagen production and renew the skin. Products with antioxidants, such as vitamin C and niacinamide, also protect the skin from damage and improve its texture.
- Microneedling: Also known as collagen induction therapy, microneedling involves creating micro-injuries in the skin using fine needles. This stimulates the body’s natural wound-healing process and also boosts collagen and elastin production. Devices such as the Dermaroller and Dermapen have made this treatment even more accessible and effective.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma therapy), also known as a vampire facial, involves extracting a small amount of the patient’s blood, which is then processed to concentrate the platelets. Once the platelets are concentrated, the PRP is injected back into targeted areas of the skin. The high concentration of growth factors in PRP stimulates tissue regeneration and boosts collagen production, helping to improve skin texture, reduce fine lines and wrinkles, and enhance overall skin health. This natural, regenerative process makes PRP a popular choice for those seeking a more youthful and rejuvenated appearance without invasive treatments.
Latest Scientific Studies On Wrinkles
Recent scientific studies continue to explore and validate new treatments and understandings of wrinkle formation and prevention. Here are a few key findings:
Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell therapy is emerging as a promising approach in the field of anti-ageing and skin rejuvenation. Studies have demonstrated that stem cell-based treatments can effectively rejuvenate ageing skin by promoting the regeneration of skin cells and enhancing the production of collagen and elastin, which are vital for maintaining skin firmness and elasticity. Research has particularly focused on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), which have shown potential in reversing signs of ageing by stimulating natural healing processes. These stem cells can differentiate into various types of skin cells, contributing to the repair of damaged tissue and improving overall skin quality. While clinical trials are ongoing, early results are promising, suggesting that stem cell therapy could become a key tool in combating skin ageing, provided that safety and efficacy are thoroughly established.
Gene Therapy: Advances in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, are revolutionising the potential for targeted anti-ageing treatments. Gene therapy aims to address the root causes of skin ageing at the molecular level by targeting specific genetic factors that regulate collagen production and other critical processes involved in skin health. The technology allows for the precise repair or replacement of damaged genes responsible for collagen synthesis, potentially reversing or slowing down the ageing process. Although research in this area is still in its early stages, the possibilities for gene therapy in dermatology are vast. If successful, these treatments could offer a revolutionary approach to skin rejuvenation, providing long-term solutions by correcting the genetic underpinnings of ageing rather than merely addressing the symptoms.
Antioxidant Therapy: Antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting the skin from environmental damage, oxidative stress, and the harmful effects of free radicals. Recent studies have highlighted the effectiveness of antioxidants like resveratrol, coenzyme Q10, and ferulic acid in reducing wrinkles and improving skin health. These compounds work by neutralising free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and accelerate the ageing process. Antioxidants also support cellular repair and regeneration, helping to maintain a youthful appearance. Ongoing research continues to explore the potential of antioxidant therapy in enhancing skin resilience, with newer formulations being developed to maximise their efficacy and penetration into the deeper layers of the skin.
Peptide Research: Peptides are short chains of amino acids that play a vital role in signalling cellular processes, including the production of collagen and other structural proteins. Recent research has focused on bioactive peptides that can stimulate collagen synthesis, improve skin barrier function, and enhance hydration, making them valuable components in advanced skincare formulations. Peptides like matrixyl, copper peptides, and palmitoyl pentapeptide are among those being incorporated into products aimed at reducing the appearance of fine lines, boosting skin firmness, and promoting overall skin health. These peptides work by communicating with skin cells to encourage repair and regeneration, effectively mimicking the body’s natural processes for maintaining youthful skin.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Dermatology: AI and machine learning are transforming the landscape of personalised skincare by providing insights that were previously difficult to attain. These technologies analyse a vast array of factors, including individual skin types, environmental conditions, and lifestyle habits, to develop customised skincare regimens and predict the efficacy of anti-ageing treatments. AI algorithms can process data from thousands of clinical studies, consumer feedback, and real-world results to recommend targeted treatments and products tailored to each individual’s needs. This personalised approach has the potential to significantly improve the outcomes of wrinkle reduction therapies and other anti-ageing treatments, offering a level of precision and effectiveness that was previously unattainable with traditional methods. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into dermatology and aesthetics is expected to grow, further refining the science of skincare.
Preventing Wrinkles
While it is impossible to completely stop the ageing process, there are ways to slow down the formation of wrinkles and keep skin looking youthful for longer.
- Sun Protection: The best way to prevent wrinkles is to protect your skin from the sun. Wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on cloudy days, can protect the skin from harmful UV rays.
- Skincare Regimen: A good skincare routine can help reduce the appearance of wrinkles and slow their development.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking accelerates skin aging, so quitting is one of the most effective ways to prevent wrinkles from forming. Avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke is also important, as it can have similar effects on the skin.
- Minimise Stress: Chronic stress can lead to the breakdown of collagen and elastin in the skin, contributing to the formation of wrinkles. Practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or yoga, can help keep both the mind and skin healthy.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing premature wrinkles. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support skin health. Staying hydrated, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly also play a significant role in keeping the skin looking youthful.

Navigating The Science Of Skin Ageing
Wrinkles are a complex result of both intrinsic and extrinsic ageing processes. However, advancements in skincare and medical treatments offer a wide range of options for those looking to reduce their appearance and maintain youthful skin. There is no final cure but wrinkle reduction is a reality.
From non-invasive technologies and injectable treatments to innovative topical formulations and emerging therapies like stem cell and gene treatments, the future of wrinkle treatment looks promising. Understanding the science behind wrinkles and staying informed about the latest research and treatments can help individuals make educated decisions about their anti-ageing strategies.


