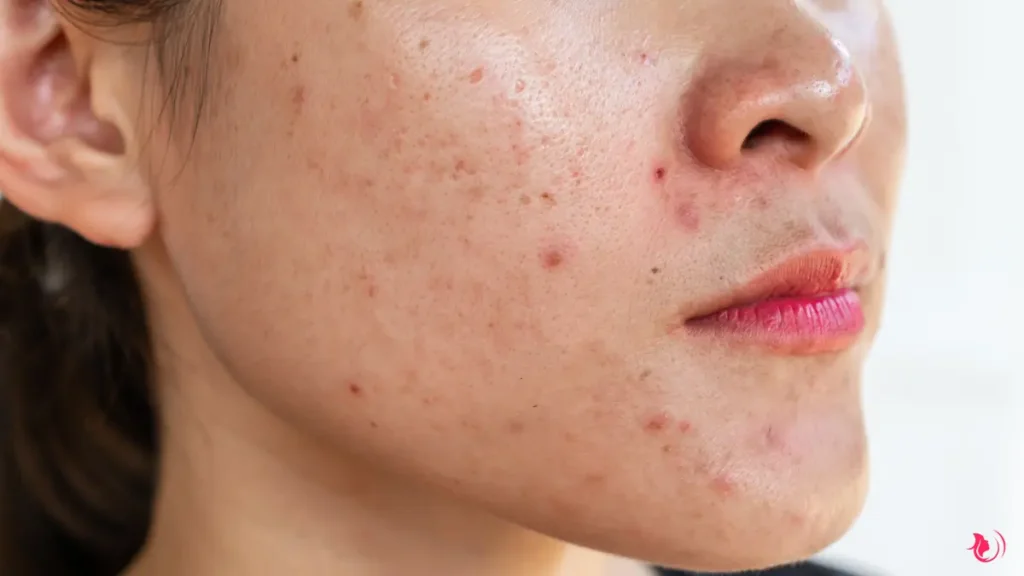
Acne scars are permanent textural changes and indentations that occur on the skin as a result of severe acne. When the skin’s pore swells from an acne lesion, the follicle wall can break. If the rupture is deep, the infected material can spill out into the surrounding tissue, causing deeper lesions. The skin attempts to repair these lesions by forming new collagen fibres. However, the skin’s repair process is not always perfect, leading to the formation of scars.
Types of Acne Scars
There are several types of acne scars, each with distinct characteristics:
- Atrophic Scars: These scars are the most common and are typically caused by a loss of tissue. They can be further classified into three types:
- Ice Pick Scars: Deep, narrow, and pitted scars that resemble the appearance of having been punctured by a sharp object.
- Boxcar Scars: Broad, box-like depressions with sharply defined edges. They are usually wider than ice pick scars and give the skin a pitted appearance.
- Rolling Scars: Have a wave-like appearance across the skin, caused by bands of scar tissue that form under the skin, giving it a rolling or undulating look.
- Hypertrophic Scars: These scars are raised above the surface of the skin due to excess collagen production during the healing process. They often appear red and can be itchy or painful.
- Keloid Scars: Similar to hypertrophic scars but more severe, keloid scars are thick, raised scars that can extend beyond the original wound area. They are the result of an overly aggressive healing process and can continue to grow over time.
Causes of Acne Scars
Acne scars can be caused by several factors, each contributing in different ways to the formation and severity of these scars. One of the primary causes is inflammation. Severe inflammation from acne lesions damages the skin’s underlying structure, disrupting the collagen and tissue in the affected area. This damage can lead to the skin attempting to repair itself, but the process often results in the formation of scars instead of smooth, healthy skin.
Another significant factor is delayed treatment. When acne is not treated promptly or adequately, it can lead to prolonged inflammation and deeper, more extensive damage to the skin. This increases the likelihood of scarring, as the skin’s ability to heal effectively diminishes over time. Early and effective treatment of acne is crucial in preventing scars from forming and minimizing their appearance.
Genetics also play a role in the development of acne scars. Some individuals are more genetically predisposed to scarring than others. Their skin may react more intensely to inflammation, or they may have a natural tendency for their skin to form scars during the healing process. Understanding one’s genetic predisposition can help in taking proactive measures to manage acne and prevent scarring.
Lastly, picking or squeezing pimples can significantly exacerbate the risk of scarring. This common habit can cause additional trauma to the skin, increasing inflammation and disrupting the healing process. By manually interfering with acne lesions, individuals can inadvertently push bacteria and debris deeper into the skin, leading to more severe damage and consequently, more pronounced scars. Avoiding this behaviour is essential for allowing acne to heal properly and reducing the risk of lasting scars.
Treatment Options
There are various treatments available to improve the appearance of acne scars, depending on the type and severity:
- Topical Treatments: Products containing retinoids, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) can help improve skin texture and promote cell turnover.
- Chemical Peels: These can help reduce the depth of acne scars by removing the outer layer of skin and promoting new skin growth.
- Microdermabrasion and Dermabrasion: These procedures exfoliate the top layers of skin, encouraging new skin growth and reducing scar visibility.
- Microneedling: Involves using fine needles to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin, stimulating collagen production and improving skin texture.
- Laser Therapy: Different types of lasers can be used to resurface the skin, reduce redness, and stimulate collagen production.
- Fillers: Injectable fillers can temporarily plump up atrophic scars, making them less noticeable.
- Surgery: Procedures like punch excision or subcision can be used to remove or break up scar tissue.
Preventing Acne Scars
Preventing acne scars involves effective acne management and proper skincare practices:
Treat Acne Early
One of the most effective ways to prevent acne scars is to treat acne early and effectively. Addressing acne promptly can prevent severe inflammation that often leads to scarring. Consulting a dermatologist at the first sign of acne can help tailor a treatment plan that suits your skin type and acne severity. Early treatment can include topical medications, oral antibiotics, or hormonal treatments that reduce breakouts and inflammation. By controlling acne early, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing deep, persistent scars.
Avoid Picking or Squeezing
While it may be tempting to pick or squeeze pimples, doing so can cause additional damage to your skin. Picking at acne lesions can push bacteria deeper into the skin, increasing inflammation and the likelihood of scarring. Moreover, it can create open wounds that are prone to infection and slow the healing process. Instead, it’s best to leave acne treatments to professional dermatologists and use recommended over-the-counter or prescription products to manage breakouts. Keeping your hands off your face and maintaining a hands-free skincare routine can minimize the risk of permanent marks.
Use Sun Protection
Sun exposure can exacerbate acne scars by darkening them, making them more noticeable, and prolonging the healing process. UV rays trigger the production of melanin, which can darken post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and other types of scars. To protect your skin, it’s crucial to incorporate a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 into your daily skincare routine, even on cloudy days. Additionally, wearing protective clothing and seeking shade can further shield your skin from harmful UV rays. Consistent sun protection helps prevent the worsening of existing scars and reduces the risk of developing new ones.
Follow a Skincare Routine
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine is essential for managing acne and reducing the risk of scarring. A well-rounded routine includes gentle cleansing to remove dirt, oil, and impurities without stripping the skin of its natural moisture. Regular exfoliation with mild acids like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) can help unclog pores and promote cell turnover, preventing acne formation and improving skin texture.
Moisturising is also crucial, as it keeps the skin hydrated and supports its natural barrier function. Using non-comedogenic and fragrance-free products can minimize irritation and breakouts. Additionally, incorporating treatments like retinoids or vitamin C serums can boost collagen production and enhance skin repair, further reducing the appearance of scars.
Understanding acne scars and their treatments is essential for managing their appearance and improving skin health. Consulting a dermatologist can help in selecting the most appropriate treatment options based on individual skin types and scar characteristics.